You start with one AI agent to save time. A month later, you've got prompts in a doc, outputs in Slack, half-finished automations in three places, and the same request getting handled a dozen different ways depending on who saw it first. That's what happens when businesses try to "do AI" by building roughly 43 agents with no plan in place to coordinate them.
AI agent orchestration solves this problem. Instead of relying on a single, general-purpose AI agent to do everything (which rarely works), AI agent orchestration lets organizations tailor different AI agents to specific tasks and then bring them together to work as a cohesive team.
To help you think about AI agent orchestration, here's a quick breakdown of what it is, why it matters, and how you can easily build multi-agent systems with no code using Zapier.
Table of contents:
What is AI agent orchestration?
AI agent orchestration coordinates multiple AI agents—each specialized for a certain task—ensuring they communicate, share context, and adapt collectively to achieve whatever goal you've set. It's basically project management for robots.
As with flesh-and-blood human beings, the absence of orchestration forces AI agents to operate in silos, solving narrow problems in splendid isolation (while generating three new ones just out of frame). This works fine for routine tasks but falls apart when you need to tackle larger, more intricate processes. Agentic orchestration bridges these gaps by enabling scalable, real-world applications that a single AI simply can't pull off (at least with today's models).
If this sounds compelling, Zapier Agents can substantially reduce the friction of establishing agentic orchestration, with no coding necessary. Add AI agents directly to your workflows, connect them to each other and the rest of your tech stack, and start automating tasks like triaging customer requests, qualifying sales leads, and generating reports.
How does AI agent orchestration work?
Setting up agentic AI orchestration doesn't have to feel like assembling IKEA furniture blindfolded (not judging how you spend your weekends). The details will vary by context, of course, but by and large, the underlying process will look something like this.
1. Assessment and planning
First, identify the workflows or processes where AI agent orchestration can help. This could be customer support ticket routing, lead qualification, or anything in between, but you should always think about whether a simple agent could handle the job.
If you have a single, narrowly-defined task, a simple workflow, or you're concerned about cost and system complexity, one agent is probably the way to go. Otherwise, agent orchestration might be the solution you need.
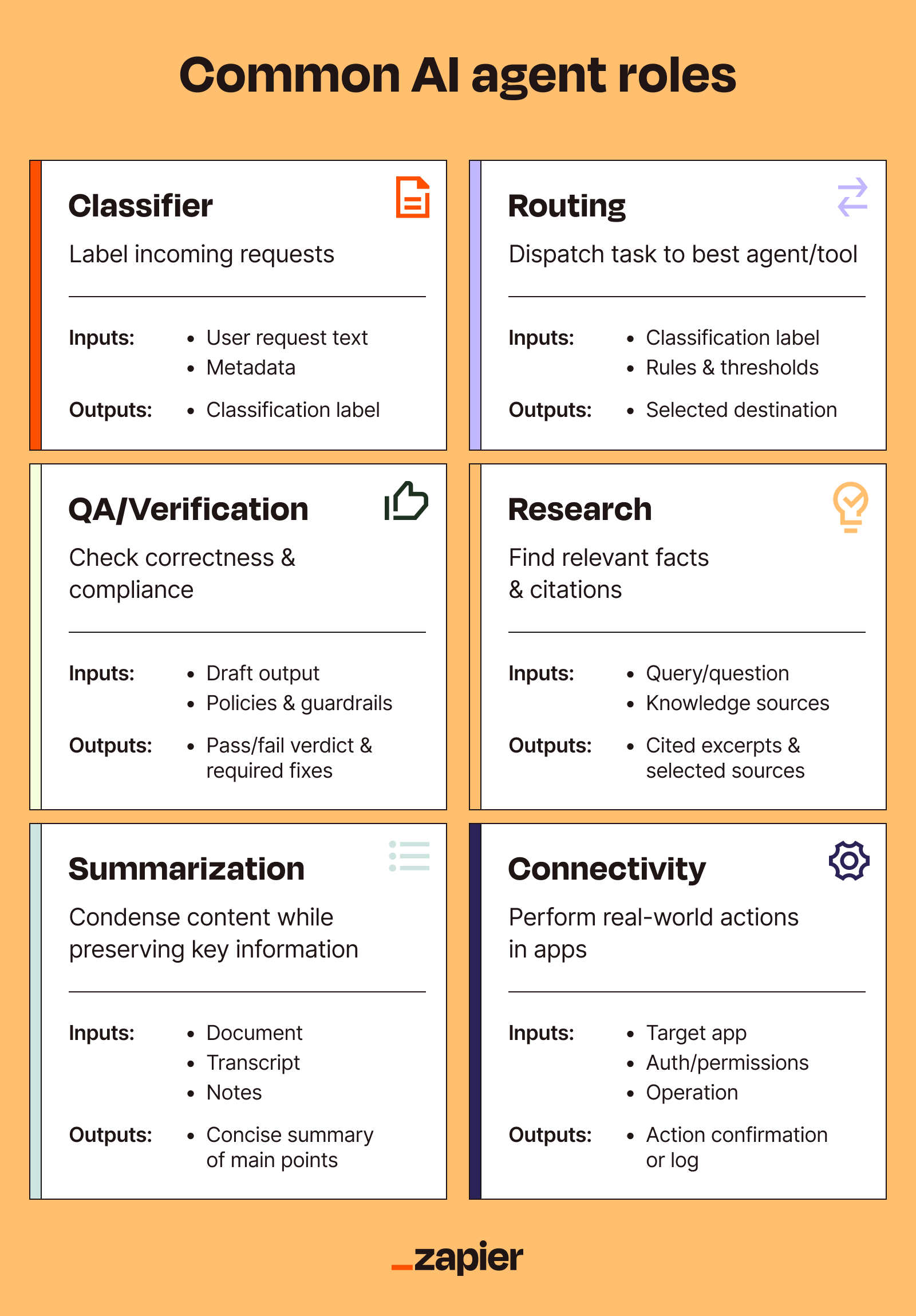
2. Selection of specialized AI agents
The FBI and your AI engineer may not have all that much in common, but they both need the right agent for the right job (and they're both definitely tracking your internet history). Each agent should excel at a specific task, whether that's analyzing data, generating insights, or triggering one part of a sequence of actions.
The more you can drill down into a specific, well-defined, un-screw-uppable task, the more success you'll have building and using an agent for it. This matters because, compared to humans, AI systems are still pretty bad at handling ambiguity, uncertainty, and fork-in-the-road scenarios. But if you can divvy up the work well enough, you can create a whole ecosystem of agents that, when woven together with orchestration platforms, becomes way more capable than any single agent could be.
For example, with Zapier Agents, you could build one agent that qualifies incoming leads from forms, one that researches each lead's company, and one that drafts personalized outreach emails—then connect them so it all flows automatically.
3. Orchestration framework implementation
With your agents chosen, you'll need an implementation tool like Zapier, which lets you build AI agents and orchestrate them as part of end-to-end business processes. If individual agents are like musicians in an orchestra, this framework acts as the conductor of your broader AI symphony.
4. Agent connection and coordination
Once the agents are in place, define the sequence and conditions under which they'll operate to create smooth handoffs and consistent outputs.
With Zapier, for example, you have a simple interface that allows you to program different agents, powered by AI, aimed at particular tasks. Agents can interact with each other, meaning you can create a series of them to tackle discrete parts of a complex workflow—each agent completes its task and passes output to the next node in the chain.
This sounds more complicated than it actually is, and you can build multi-agent systems on Zapier in minutes using templates and natural language prompts.
5. Data sharing and context management
Enable agents to share data and maintain context across interactions. This prevents duplication of effort and ensures continuity throughout the workflow.
There are many ways to do this, but a common one is to create a data store containing things like instructions, documents, and customer history, which different agents access as part of a retrieval-augmented generation system.
Depending on the tool you use, you might need a vector database, but on Zapier, you can easily upload or connect as many knowledge sources as you'd like.
6. Continuous optimization and learning
Monitor the performance of your agent swarm (which can degrade for any number of different reasons) and work to refine the enterprise AI agent orchestration over time. As your agents (and you) learn and adapt, your system can become vastly more efficient, but only if you're keeping a careful eye on things.
Most automation platforms allow you to track how data flows through your system, what each agent does with it, and where potential problems arise. Usually, that's enough, but you might eventually need dedicated observability tools to get really granular.
Why is AI agent orchestration important?
Imagine heading a business where every department uses its own tools—none of them talk to each other. The Macs and PCs can't communicate, Linux folks are running different distributions (and won't shut up about it), and not a single power cord works on a different machine.
Does this sound familiar? Hold this image (and all the rage-induced heartburn that comes with it) in mind as you read the benefits that come from effective AI agent orchestration.
Operational efficiency gains: Well-orchestrated AI agents automate and streamline multi-step workflows, reducing manual intervention and handoffs. When tasks are completed in an optimal sequence, troublesome bottlenecks get minimized or eliminated altogether.
Cost reduction: Greater efficiency means lower operational, staffing, and integration costs. Also, computational resources get used more effectively, leading to further expense reductions.
Scalability improvements: Once you've ironed out the subtleties of orchestration, adding or reconfiguring agents is relatively straightforward—especially with a tool like Zapier that makes it easy to connect to new apps, hook up new data sources, and pipe output to additional agents. This means you can adapt to higher workloads or new processes without having to tear down your entire system and start over.
Error reduction and consistency: Most AI agent orchestration frameworks allow for guardrails that channel agent activity along well-defined paths, reducing mistakes, rework, human intervention, and inconsistencies between data stores.
Enhanced decision-making: Agents share and synthesize information quickly, enabling real-time analysis and coordinated responses. As long as you keep latency low, responsiveness will improve significantly.
Boosts automation potential: Coordinated agents expand automation from simple tasks (composing emails) to complex, cross-functional processes (summarizing months of work and contextualizing it for specific teams), unlocking new opportunities across departments.
Resource optimization: With orchestration, computational resources, agent focus, and data access get allocated efficiently. Rather than running the risk of redundant agents wasting time (or a swarm of agents working on tasks that add exactly zero value to your business), you can track your agents and their tasks, maximizing ROI across the system.
Reduced AI sprawl: Orchestration prevents fragmented deployments, ensuring all AI agents operate within a unified framework. When done correctly, this improves visibility and integration because a single set of rules applies across all agents and contexts.
More reliable governance and compliance: Centralized control ensures adherence to regulatory requirements, ethical guidelines, and company policies. This matters because, like it or not, AI is becoming more common in everyday life, but also because regulatory frameworks keep changing. Having everything in one place makes it much easier to check against compliance requirements.
Types of AI agent orchestration
AI agent orchestration comes in several varieties, and which one makes the most sense depends (say it with me) on your needs:
Centralized orchestration: A single orchestrator agent acts as the "brain," directing others and ensuring consistency. This approach is superior if you're after predictability in your workflows.
Decentralized orchestration: With decentralized orchestration, agents communicate directly and make independent decisions. This brings certain challenges (the system can get stuck in unproductive loops), but it also enhances scalability and resilience because no single failure can bring the whole system down.
Hierarchical orchestration: Hierarchical orchestration arranges agents in layers (a hierarchy, if you will), balancing strategic control against task-specific execution. This is basically how every corporation is already organized, so at least the concept is familiar.
Federated orchestration: This is a newer approach where independent agents or organizations collaborate without fully sharing data, making it perfect for industries with strict privacy regulations. The trade-off is that this is more complex to set up and maintain.
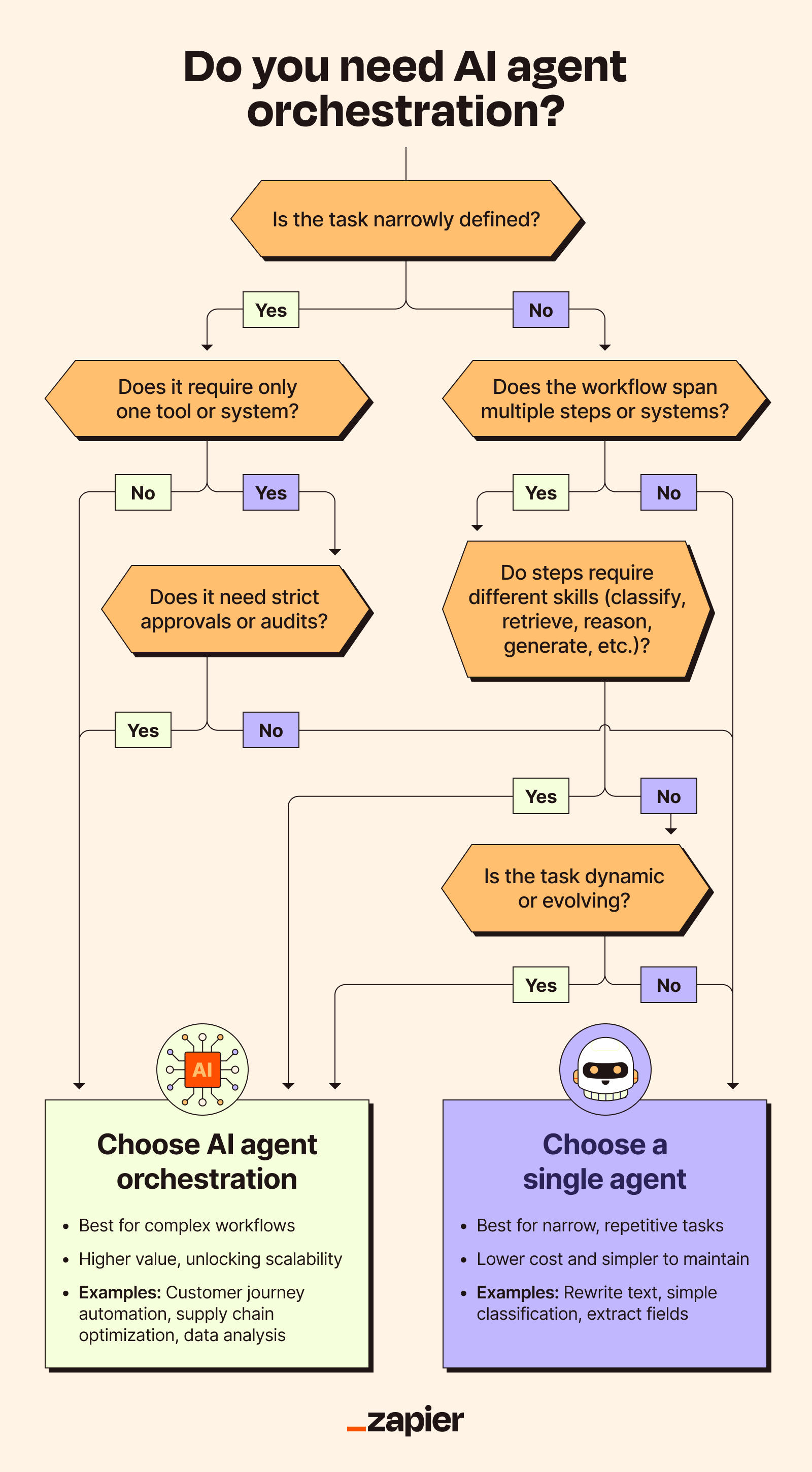
AI agent orchestration vs. related concepts
It's worth clarifying how AI agent orchestration compares to similar practices. Though it's distinct from other techniques for syncing up computing technologies, it's easy to confuse the terminology—which can lead to the very friction and siloing we're trying to avoid.
With that in mind, here are some things that are kinda-sorta like AI agent orchestration, but different enough to warrant their own terms.
AI agent orchestration vs. AI orchestration
AI agent orchestration is a subset of AI orchestration, which encompasses the broader application of AI tools, agents, and automations across workflows. AI orchestration itself is a subset of software orchestration, all aimed at creating seamless, intelligent systems—and tools like Zapier are great for orchestration work of every kind, whether you're dealing with AI agents specifically or just trying to integrate your various software tools.
AI agent orchestration vs. multi-agent orchestration
While some view multi-agent orchestration as more advanced, the two terms largely overlap. The key difference is scope—multi-agent orchestration often involves coordinating agents across diverse environments, which adds substantial challenges but also expands the range of activities an agent swarm can undertake.
AI orchestration vs. traditional AI apps
Traditional AI applications are standalone tools designed to perform specific tasks using artificial intelligence. A chatbot might answer customer questions, a recommendation engine could suggest products, and so forth.
In contrast, AI agent orchestration takes a broader approach by linking multiple AI systems to manage complex, end-to-end processes. Instead of working in isolation, orchestrated AI agents collaborate to handle multi-step workflows. An orchestrated system could use a chatbot to pass complex queries to a specialized problem-solving AI.
With tools like Zapier, anyone can set up these sophisticated workflows without deep technical expertise.
AI orchestration vs. MLOps
MLOps (machine learning operations) focuses on managing the lifecycle of individual machine learning models, including model development, deployment, monitoring, and maintenance.
An AI orchestration engine like Zapier takes a higher-level view, coordinating complex workflows that may involve multiple ML models, AI agents, APIs, databases, and more. MLOps ensures specific models function as expected, while AI orchestration ensures these models integrate seamlessly into larger, automated systems.
Examples of AI agent orchestration
Once you understand the mechanics of orchestration, seeing it in action makes the value clearer. AI agent orchestration tends to pay off when:
A single task can branch into multiple specialized workflows
You need tight control over which agents can take risky actions
Several triggers need to funnel into one complex workflow
Here are three real-world patterns that show what AI agent orchestration looks like in practice. These are all based on actual multi-agent systems that the Zapier team uses.
Email triage with role-based routing
This support system reviews incoming emails and routes them to specialized handlers based on complexity and topic.
Agents:
Router agent reads each email and decides which category it falls into
Specialist agent for basic inquiries handles straightforward questions
Technical agent troubleshoots product issues
Escalation agent manages high-priority or sensitive cases
How orchestration works: Permissions stay tight on purpose. For example, only the escalation agent can perform high-risk actions like deleting records or modifying accounts, which reduces the chance of accidental damage from other agents that run more frequently and have broader instructions.
Built with Zapier: An email trigger kicks off the router agent, which evaluates the message and passes the full context to the appropriate specialist agent. That agent can update your CRM, create or close tickets, and notify relevant team members in Slack.
Feature guide content pipeline
Here, a documentation system researches, drafts, and edits long-form feature guides with minimal human intervention.
Agents:
User insights researcher mines community forums for common questions and pain points
Use case researcher pulls practical workflow examples from internal documentation
Writer agent assembles a structured first draft using a preset template
Four editor agents each refine a specific editorial dimension (clarity, tone, accuracy, structure)
How orchestration works: This is a sequential handoff chain. Each agent does one job, then passes better context to the next one in line. The research agent gathers raw material, the writer turns it into a coherent draft, and the editor agents polish specific aspects without stepping on each other's toes. You still keep a human review step at the end, but the repetitive research and structuring work is largely handled upstream.
Built with Zapier: A form submission (containing the feature name, notes, and relevant doc links) triggers the first research agent. Each agent deposits its output into a shared data store (like Zapier Tables), which the next agent reads from and builds on. After the final editor runs, a Zap (automated workflow) creates a Google Doc with the finished draft and drops the link in Slack for review.
Multi-channel task consolidation
This personal productivity system captures to-dos from Slack emoji reactions, direct messages, and Gmail labels, then funnels them into one central scheduling agent.
Agents:
Slack emoji intake agent monitors for the "to-do" emoji reaction
Direct message intake agent processes tasks sent via chat
Gmail intake agent watches for emails tagged with a "to-do" label
Scheduling agent creates tasks and blocks time on your calendar
How orchestration works: This is a convergent pattern where multiple intake agents feed one scheduling agent. The intake agents normalize different input formats (emoji metadata, chat messages, email subjects) and pass structured data downstream. Then the scheduling agent handles the complicated calendar logic once, instead of duplicating it across three separate workflows.
Built with Zapier: Three separate triggers—emoji reaction watcher, incoming webhook for DMs, and Gmail label monitor—each activate their own intake agent. Those agents extract the important details and pass structured data to the scheduling agent, which writes to your task manager and finds slots in your calendar based on priority and estimated duration.
Getting started with AI agent orchestration
If you're ready to dive deeper into AI agent orchestration, start by identifying areas where disconnected AI agents are holding you back.
Then explore how Zapier makes it easy to integrate and manage AI agents across your tech stack. Build and connect different AI agents, set up workflows, manage data flow, and do all the orchestration stuff we've been talking about, without any code.
For a faster start, choose a Zapier agent template from our curated collection. Choose from prebuilt, customizable agents for common workflows like lead enrichment or customer sentiment analysis that can be deployed in minutes.
Related reading: